It may look like a regular slot machine and play like one, but a video lottery terminal differs quite a bit in terms of how winners are determined. VLT gaming machines are usually equated more with games like bingo, pull-tabs, scratch-offs, or lotto than they are with slot machines. This is because there are a pre-determined number of winners. EE2355 DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES SCE 1 of 144 ELECTRICAL AND ELECTRONICS ENGINEERING A Course Material on DESIGN OF ELECTRICAL MACHINES. Selecting rotor slots of squirrel cage machines – Design of rotor bars & slots – Design of end rings. Determination of full load field mmf – Design of field winding – Design of turbo. If the load resistance is 12 Ω, determine the terminal voltage of the machine. A separately excited dc generator, when driven at 1 500 rpm, supplies a load current of 200 A at 250 V to a circuit of constant resistance.
Lecture Hours
- Monday 9:40-12:30 Dz-17
Brief Info:
This course covers basic design principles of electrical machines. You will be able to design main parameters of an electric machine such as magnetic and electric loading, number of slots, winding dimensions. Thermal and structural design of electric machines will be also covered. You will use FEA software and optimization tools to determine the best parameters.
Textbooks
- Design of Rotating Electrical Machines, Juha Pyrhonen, Tapani Jokinen, Valeria Hrabovcova, 2009
Grading:
- 1st Project: 15%
- 2nd Project: 20%
- 3rd Project: 25%
- Final: 30% (Open Book)
- Participation: 10%
Presentations:
- Week#2 (15/02): Review of Magnetic Circuits
- Week#3 (26/02): Practical Materials
- Week#5 (12/03): Transformer Design
- Week#6 (19/03): Windings of Electrical Machines
- Week#8 (02/04): Technical visit to Emtas
- Week#9 (09/04): Main Machine Parameters
- Week#9 (09/04): Basic Machine Dimensions
- Week#10 (16/04): Number of slots-Machine Parameters
- Week#12-13 (30/04): Magnetizing Current - Magnetic Losses
- Week#14 (14/05): Resistance
- Week#14 (14/05): Thermal Design
Project Assignments
For details of the projects, please visit the GitHub page
- Project-1: Inductor and Transformer Design (due 28/03)
- Project-2: Induction Motor Analysis
Online References:
- Wiley Online Library: (browse using METU Library)
Software
Here you can find a few useful software on electric machine design and FEA.
Free/Open-Source
- FEMM: 2D FEA Software
- MotorAnalysis: MATLAB GUI for induction motor design
- Dolomites: An open source design tool
- Emetor Winding: A tool to calculate winding factors, harmonics etc
- SMEKLib: An open-source MATLAB library for 2D-FEA Analysis of Electrical machines
- Homebuilt electric motors: Tools for brushless PM motors
- Syre - Synchronous reluctance machine design and optimization tool
Commercial Products

- Opera FEA: 3D Electromagnetic, Thermal FEA (also models supercodnuctors)
- MagSoft: Flux, Portunus, Speed
- Motor-Design: EM and lumped thermal analysis
- Quick Field: Free Student edition
- Emetor: Cloud FEA, free student edition
- Quick Field: Free student edition
Other Useful Links
The content below this line will be changed this semester
Presentation Topics
To be modified:
Please choose one topic from below, and fill in the online spreadsheet to book your topic and date. One topic should be presented only once. First-come first served.
The full guidelines are given at the end of this page.
- Doubly-fed induction generators
- Linear permanent magnet machines
- Wave energy power take-off systems
- Direct-drive wind turbine generators
- Ultra-high speed machines
- Superconducting machines
- Very large synchronous machines (>50 MVA)
- Micro-machines
- Electric motors used in electric cars
- Fault-tolerant electric machines
- Spherical and conical electric machines
- Modular (with soft magnetic composite) machines
- PM assisted reluctance motors
- Axial flux PM machines
- Magnetic gear systems (Magnomatics)
- Synchronous reluctance motors
- Motors used in electric traction
- Space rated electric motors
- Brushless DC machines
- Condition monitoring of electrical machines
Multi-phase (ie. 5-9 etc) machines
- You are allowed to swap presentations dates later, but if you miss your scheduled slot, you will get 0.
- Presentation duration: 12 minutes (+5 minutes for QA).
You will be evaluated by you classmates using the following score sheet
An ideal presentation should cover the following aspects:
- Main working principles of the machine
- Fundamental differences from other type of machines
- Application Areas
- Advantages/Disadvantages
- You should prepare a handout for the audience. Please note that handouts are not the printed version of your slides. They should be in parallel with your slides, but should have more information. At the end of the handouts, there should be a reading list(5-6 papers, books) for detailed information on the topic.
- If you use other people’s work (data, photo, table etc.), please cite them in your presentation. Plagiarism will not be tolerated.
- When preparing the slides, please have a look at these links:
Third Project Topics (Deadline:15/06)
The main idea of this project is to get you familiar with FEA (finite element analysis) methods. You have the following options:
A- Modelling Your 2nd Project Designs in FEA
You are supposed to model the induction machines you designed in the 2nd projects. You are free to use any FEA software, but I advise you to use Maxwell. The outputs of the projects are as follows:
- Model your design to RMxprt.
- In the RMxprt get the performance metrics such as: (torque vs. speed, flux in the airgap, cogging torque etc).
- Export your design into Maxwell 2D (don’t bother with 3D simulations)
- In 2D FEA show the flux density distribution, flux vectors. Calculate the flux densities in the critical parts (tooth, back core etc)
- Also I expect you to comment on general design considerations that you learnt throughout the course.
B- Direct-Drive PM Generator Design
If you are tired of designing induction machines, you have another option: to design a direct-drive permanent magnet generator for a wind turbine. Here are the specifications:
- Rated Power: 50 kW, Rated Speed: 60 rpm
- Surface mounted, radial flux type PM generator
- Outer Diameter < 1.5 m
- Total Mass < 1000 kg
C- BMW i3 Synchronous Reluctance Motor Design
You are supposed to design a synchronous reluctance motror for the BMW i3, which is a full-electric car with a hybrid-synchronous motor. Although the motor is rated at 75 kW, it can produce instantaneous power up to 125 kW, and torque up to 250 Nm. Although the original motor is PM assisted, you can design a classical synchronous reluctance motor. You are free to use any software, but I personally advise you to use SYRE. Here are some useful links:
Other remarks for the 3rd projects:
- There will NOT be any number of commits grading. Only the technical merits will be graded.
- Please do NOT upload your FEA models to Github. Only upload your figures and reports. I prefer IPython notebooks, but it is ok to use Markdown, Word etc.
- I know Project-B and Project C are more challenging than using the previous induction motor design, but I will grade your project accordingly. Therefore, in project-B and project-C, it is ok to have your designs less detailed compared to project-A.
Second Project Topics (Deadline:11/05)
In this projects you are supposed to design an induction motor (the options are given below). In this project you will use Motor Analysis, a MATLAB GUI for induction motor design. Please spend some time to learn the software and read the documentation.
Here are the projects:
A- Design of a Train Traction Motor
The motor you need to design is a traction asynchronous squirrel cage induction motor with the following specifications:
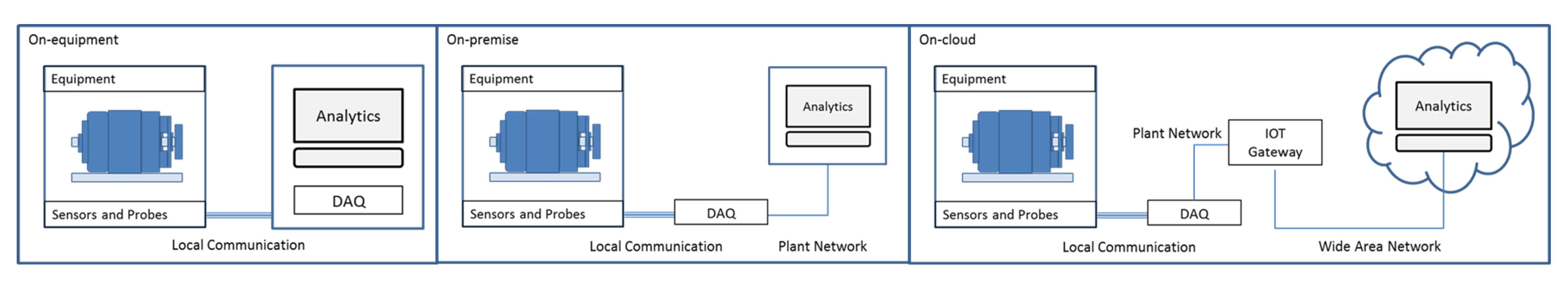
- Rated Power Output: 1280 kW
- Line-to-line voltage: 1350 V
- Number of poles: 6
- Rated Speed: 1520 rpm (72 km/h) (driven with 78 Hz inverter)
- Rated Motor Torque: 7843 Nm
- Cooling: Forced Air Cooling
- Insulating Class: 200
- Train Wheel Diameter: 1210 mm
- Maximum Speed: 140 km/h
- Gear Ratio: 4.821
What Is Slot Loading In Electrical Machines Machine
B- Tesla Model S Induction Motor
Design the induction motor that is used in Tesla Model S, which has a few different variations. To keep things simple, use the RWD 85 Model, with rear wheel drive, which has the following specs:
- Max. Power: 360 hp (270 kW)
- Max. Torque: 441 Nm
- Top Speed: 225 km/h
You can find some specs of the motor from here and here, you can find more information on the internet.
Here are a few useful links:

C- Wind Turbine Induction Generator
You are required to design a squirrel cage induction generator for the Northerl Energy’s VIRA-250 wind turbine. The specifications of the wind turbine are as follows:
- Rated Power: 250 kW
- Rated Wind Speed: 14 m/s
- Rated Turbine Speed: 24.3 rpm
- Gear Ratio: 31.2
- Number of Poles: 8
- Line to line voltage: 400 V
- Frequency: 50 Hz
- Rated Speed: 758 rpm
- Gearbox: (Coupled from wind turbine blade)
- Insulation Class: F
Project outcomes:
1- Design an optimized induction motor using the Motor Analysis toolbox. Additionaly, you are free to use any software listed below during your design stage.
2- Prepare a report detailing your design process (just supplying .m files is not accepted). In the report please describe how you decided on the following aspects of the prroject.
- Main Dimensions (Outer diameter, air-gap diameter, axial-length, number of slots…). Please include some basic drawings.
- Material Properties, Frame size etc.
- Magnetic Circuit Details (flux density calculations at various points: air-gap, teeth, back-core etc, magnetic loading)
- Electric Circuit (Winding selection, electric loading, fill factor, phase resistance, winding factors (for fundamentalsn and for harmonics)).
- Rough thermal calculations (cooling method, operating temperature, ways to improve cooling)
- Efficiency, current, torque characteristics
- Mass Calculations (structural mass, copper mass, steel mass etc)
3- In the second part of the report, I want you to compare at least two worse designs with the optimum design presented in the first part of your report. For example, you can vary one of the following:
- Number of rotor/stator slots
- Shape of the rotor/stator slots
- Winding diagram
- Aspect Ratio of the stator and rotor etc.
First Project Topics (Deadline: 19/04):
Here are the options for your first projects:
A- Transformer Design for a X-Ray Device:
You are supposed to design a high-frequency, high-voltage transformer that will be used in a X-Ray device. Here are some links to get you familiar with the topic:
The specs of the transformer are as follows:
- Single Phase, High Frequency High Voltage Transformer
- Primary Winding Voltage ± 417 V (peak to peak 834 V for pulsing)
- Secondary Winding Voltage ± 12.5 kV (peak to peak 25 kV for pulsing)
- Rated Power 30 kW (for maximum 100 millisecond)
- Switching Frequency Minimum 100 kHz
- Ambient Temperature 0-40 °C
B- Transformer Design for a HVDC Transmission System:
In a HVDC transmission system, DC/AC + Transformer + AC/DC system is used to step-up the DC voltage to several kV for long range transmission. Here are some links to get you familiar with HVDC Transformers:
The specs of the transformer that you are going to design are as follows:
- 6.5 MVA, Single Phase transformer
- Operating Frequency: 500 Hz
- Input Voltage: 3 kV
- Output Voltage: 300kV
- Operating Temperature 110 °C
C- Eddy Current Brake Design
In this project you are supposed to design an eddy current brake design which will be used as a mechanical damper. Here are some links on the eddy current brakes:
The eddy current brake has the following specs:
- Outer diameter smaller than 50 mm
- Axial Length shorter than 25 mm
- Required Force: 3 Nm at 1620 rpm
- Required Force: 1 Nm at 900 rpm
You don’t have to, but I strongly advise you to use a FEA software (some options are listed above) for this project.
First Project Guidelines:
You’re free to choose any of the projects. Each project has different requirements and outcomes:
Project outcomes for transformer designs:
The most important parameters are as follows (but not limited to):
- Design specifications of the core (geometry, material, total mass etc)
- Coil dimensions (number of turns, coil dimensions (in AWG), total wire length)
- Efficiency data (copper losses, core losses)
- Electrical parameters (resistance, inductance etc.)
- Comments about you chosen these parameters
Project outcomes for the eddy current brake:
- Main dimensions (diameter, length, number of poles)
- Basic drawings of the eddy current brake
- Magnet Dimensions (Type, thickness etc)
- Torque vs Speed characteristics (or verification at 900 rpm and 1620 rpm)
- Comments about the design and analysis process
Notes on Projects
Your reports has to be reproducible (i.e. it has to include codes, equations and results in a single document). The results have to be uploaded in an online repository (i.e. GitHub). For that purpose, I personally suggest IPython Notebook, which can be viewed online. However, you can also use Mathematica, RStudio or Matlab Report Generator, but not Microsoft Word.
If you are convinced to use IPython, here are some useful links:
- Install Anaconda, for a quick start on Python.
- Use Wakari, or Sage to use it online.
The source files and reports has to be uploaded to the online repository of the course (i.e. https://github.com/odtu/ee564. Have a look at this link for a quick start.
Projects Grading
Number of Commits:30%: The number of edits of your project files as seen from the contributors list. For example, if you start making your project in the last few days, you’ll get no credit. If you start early and continue editing your files, you’ll get full credit. The project topics are not easy, so this is a way to encourage to start early and work regularly.
Level of Information:50%: The detail level of your designs (see requirements above), and the accuracy of your calculations.
Report Quality:20%: Text explaining your design decisions, quality of your figures, citing relevant studies and your conclusion section.